By Niclas Dauster January 12, 2024

Bridging the Gap: Introducing MISP Airgap for Secure Environments
In an era where cybersecurity threats are ever-evolving, the need for robust and secure information sharing platforms is paramount. Enter MISP (Threat Intelligence Sharing Platform), a renowned tool in the cybersecurity arsenal. But how do you deploy such a critical tool in the most secure environments, those that are air-gapped from the outside world? This is where the MISP airgap project comes into play.
Understanding Air-Gapped Environments
Before diving into the MISP airgap project, let’s understand what an air-gapped environment is. An air-gapped environment refers to networks or systems that are completely isolated from the internet or any other unsecured networks. This isolation makes them extremely secure, as it’s incredibly difficult for external attackers to gain access. However, this also poses a unique challenge: how do you update and maintain software in a place that’s intentionally cut off from the outside world?
LXD: The Power Behind MISP Airgap
Central to the MISP airgap project is LXD, a state-of-the-art Linux containerization platform. But what exactly is LXD, and why is it crucial for the MISP airgap?
What is LXD?
LXD is an open-source container management extension of LXC (Linux Containers). It offers a user-friendly and secure way to manage containerized applications, providing an experience akin to virtual machines but with the lightweight nature of containers.
LXD’s Role in MISP Airgap
LXD is pivotal in MISP airgap for several reasons:
- Facilitates Creation and Management of Containers: LXD allows for the creation and management of isolated MISP instances and their databases in containers, ensuring each instance is self-contained and secure.
- Enables Container Image Creation: LXD’s functionality includes the ability to create container images making the movable between different systems. This is crucial in air-gapped environments where downloading images directly from the internet is not an option.
Using MISP airgap to deploy MISP to air-gapped Environments
MISP airgap is a solution designed to deploy MISP in air-gapped or isolated networks. By leveraging the power of Linux containers (LXD), it ensures a secure, efficient, and manageable deployment of MISP instances. Furthermore it enables the user to frequently update their MISP instance in an environment cut off from the internet.
Deployment and Maintenance with MISP airgap
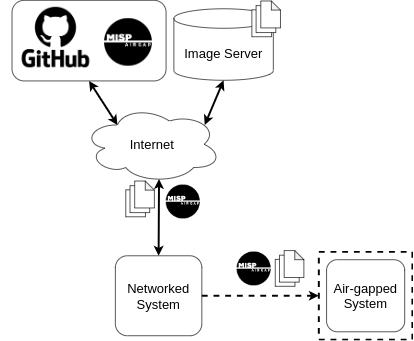
You can find detailed instructions for everything described in this section in the README file of the offical MISP airgap repository.
The overall process of deploying MISP with MISP airgap is fairly straightforward. Basically you just need to clone the MISP-airgap repository and download a couple of container images from the MISP images page on a system with internet access. Then you can transfer the repository and the images to your air-gapped system and you are ready to go.
Installation: The Magic of INSTALL.sh
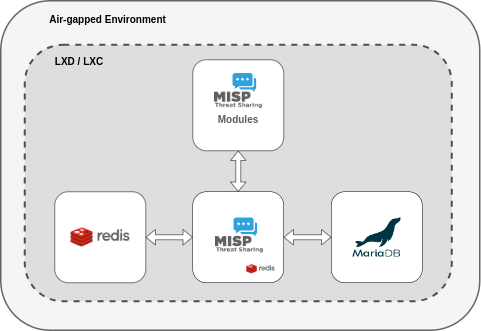
Once you have transferred all files needed, you can use the MISP-airgap INSTALL.sh script to deploy MISP. This script will create all the necessary containers for the MISP instance from the images. It will also configure them to work together to form a fully functional MISP instance with a sane default configuration. By default, this script includes the installation of MISP modules, thereby expanding the platform’s functionality. For enhanced performance of the MISP instance, the script establishes a Redis database within the MISP container. This database, accessed through a Unix socket, is exclusively allocated for session storage.
Following the installation, the script will display the login credentials and IP address for the new MISP instance. With these details, you can access and log into the MISP instance, allowing you to begin utilizing its features and start customizing it further to your needs.
Maintaining Relevance: The Role of UPDATE.sh
In the dynamic realm of cybersecurity, maintaining up-to-date systems is imperative. The unique challenges of updating air-gapped systems, which require the physical transfer of updates without the benefit of direct internet connectivity, add a layer of complexity to this task. The UPDATE.sh script is designed to address these challenges, enabling the seamless update of MISP instances. This script will update the containers to the new version and apply any necessary configuration changes as well as copy your existing MISP data and configuration to the new containers automatically. The “old” containers will be snapshoted and kept in case you need to roll back to the previous version some time in the future.
Building Images on Your Own
For organizations or users who prefer to build their images on their own, MISP Airgap accommodates this need with its build.sh script. This script allows for the creation of all images needed. These images can then be transferred to the air-gapped system and used to deploy MISP instances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, MISP airgap represents a significant step forward in the deployment of threat intelligence platforms in secure, isolated environments. By overcoming the challenges of air-gapped networks, it ensures that even the most secure organizations can benefit from the collaborative and analytical capabilities of MISP. For more detailed information about the MISP-airgapped project and its implementation, you can visit the MISP-airgap repository.
About MISP-LEA
MISP-LEA, a collaborative endeavor between Shadowserver and CIRCL, is a 24-month initiative funded by the European Union. The project’s central aim is to establish operational and enduring MISP and AIL instances dedicated specifically to law enforcement agencies.




